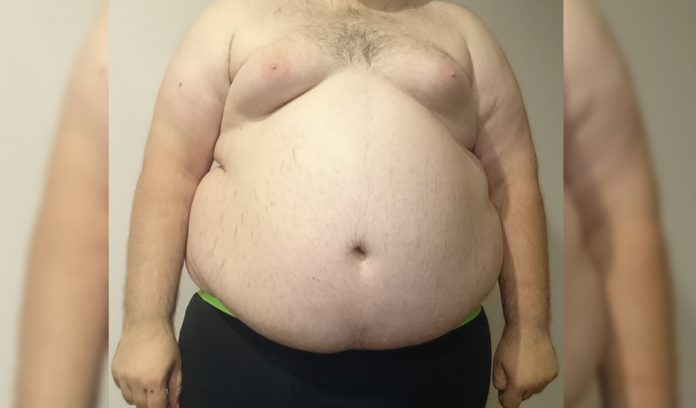
The U.S. is by far the country with one of the biggest health problems, literally, which is OBESITY. Currently, about 40% of American adults and 20% of children and teens are “clinically obese”. Those numbers don’t yet include the number of people who are simply “overweight”.
It was reported that in late 2017, the obesity epidemic in the Americas had reached another peak. But it’s not just our lifestyles which are causing this epidemic. They found out that many of the chemicals and compounds we’re exposed to have the ability to increase the risk of becoming obese. Experts who have been able to identify these compounds have given it a nickname – “obesogens”.
Good thing we still can do something about avoiding or minimizing our exposure to these damaging “obesogens” through several ways.
How do Obesogens cause Obesity?
Although the term “obesogens” was concocted way back in 2006, it was believed that these compounds actually contributed to the rise of the obesity problem even before that in most countries of the world. Obesogens are a type of endocrine disruptor which is known to disturb how the body processes and stores fat – obviously a very big problem for our health. So these compounds are making the problem much harder for us to deal with.
Obesogens, according to sources, can work on your cells in two ways: they can encourage fat accumulation by increasing the number and size of fat cells or by increasing your appetite, or they can make it more difficult for us to lose fat by changing our body’s ability to burn calories. In conclusion, obesogens are bad news for our system because they mess up with our appetite and our ability to burn up those extra calories we take in.
So how to spot an Obesogen?
More bad news! Obesogens are apparently very prolific and found in a great number of everyday products, such as pesticides, herbicides, artificial sweeteners, plastics, flame retardants, and repellant coatings on cookware and clothing, among others.
Here is a list of known obesogens identified by the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences:
- Bisphenol A (BPA) – can be found in plastics and other goods
- Pesticides
- Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) – These were used in sealants, paints, fluorescent light ballasts, adhesives, and cement in the past. PCBs are now banned but unfortunately, still persist in the environment.
- Phthalates – Used in a variety of consumer goods to make them “soft.”
- Tributyltin – A heat stabilizer for PVC pipe that’s also used as a fungicide.
- Cigarette smoke
- Flame retardants
- Air pollution
- Artificial sweeteners
Many everyday products like cosmetics and household cleaners contain obesogens. Other routes for exposure to obesogens include kitchen utensils, cookware, cleaning chemicals, and your diet – surprise!
“Obesogens can be found almost everywhere, and our diet is a main source of exposure, as some pesticides and artificial sweeteners are obesogens,” said Dr. Ana Catarina Sousa and her research group from the University of Beira Interior and the University of Aveiro.
As hard it is to weed out the products which don’t have obesogens, it is still possible to avoid them, in some ways. Here are some useful tips to avoid or reduce your exposure to obesogens:
- Choosing fresh foods instead of processed
- Buying organic fruits and veggies
- Reducing the use of plastic, especially for storing and heating food
- Choosing natural cleaning products free of obesogens
- Vacuuming and dusting more often to remove particulates
- Removing your shoes before entering your home so you don’t bring the contaminants inside
So, do you have any other tips to prevent exposure to obesogens? Share in the comments section below.








